Working with Neon read replicas
Learn how to create and and manage read replicas in Neon
Read replicas are supported with the Neon paid plans. This guide will lead you through the process of creating and managing read replicas.
The general methodology of using read replicas to segregate read-only work from your production database operations can be applied to a variety of uses cases, such as:
- Offloading analytics or reporting queries
- Distributing read requests to achieve higher throughput
- Providing read-only data access to specific users or applications who do not need to modify data
- Configuring different CPU and memory resources for each read replica for different users and applications
Regardless of the application, the steps for creating, configuring, and connecting to a read replica are the same. You can create one or more read replicas for any branch in your Neon project and configure the vCPU and memory allocated to each. Neon's Autoscaling and Autosuspend features are also supported, providing you with control over compute usage.
Prerequisites
- A Neon paid plan account
- A Neon project.
Create a read replica
Creating a read replica involves adding a read replica compute to a branch. You can add a read replica compute to any branch in your Neon project using the Neon Console, Neon CLI, or Neon API.
To create a read replica from the Neon Console:
- In the Neon Console, select Branches.
- Select the branch where your database resides.
- Click Add Read Replica.
- On the Add new compute dialog, select Read replica as the Compute type.
- Specify the Compute size options. You can configure a Fixed Size compute with a specific amount of vCPU and RAM (the default) or enable autoscaling by configuring a minimum and maximum compute size. You can also configure the Suspend compute after inactivity setting, which is the amount of idle time after which your compute is automatically suspended. The default setting is 5 minutes.
note
The compute size configuration determines the processing power of your database.
- When you finish making your selections, click Create.
In a few moments, your read replica is provisioned and appears on the Computes tab on the Branches page. The following section describes how to connect to your read replica.
Connect to a read replica
Connecting to a read replica is the same as connecting to any branch, except you connect via a read replica compute instead of your primary read-write compute. The following steps describe how to connect to your read replica with connection details obtained from the Neon Console.
-
On the Neon Dashboard, under Connection Details, select the branch, the database, and the role you want to connect with.
-
Under Compute, select a Replica.
-
Select a connection string or a code example from the drop-down menu and copy it. This is the information you need to connect to the read replica from you client or application.
A psql connection string appears similar to the following:
postgres://[user]:[password]@[neon_hostname]/[dbname]If you expect a high number of connections, select Pooled connection to add the
-poolerflag to the connection string or example.No write operations are permitted on a connection to a read replica.
View read replicas
You can view read replicas using the Neon Console or Neon API.
To view read replicas for a branch, select Branches in the Neon Console, and select a branch. Under the Computes heading, the Type field identifies your read replicas. Read replicas have a R/O value instead of R/W.
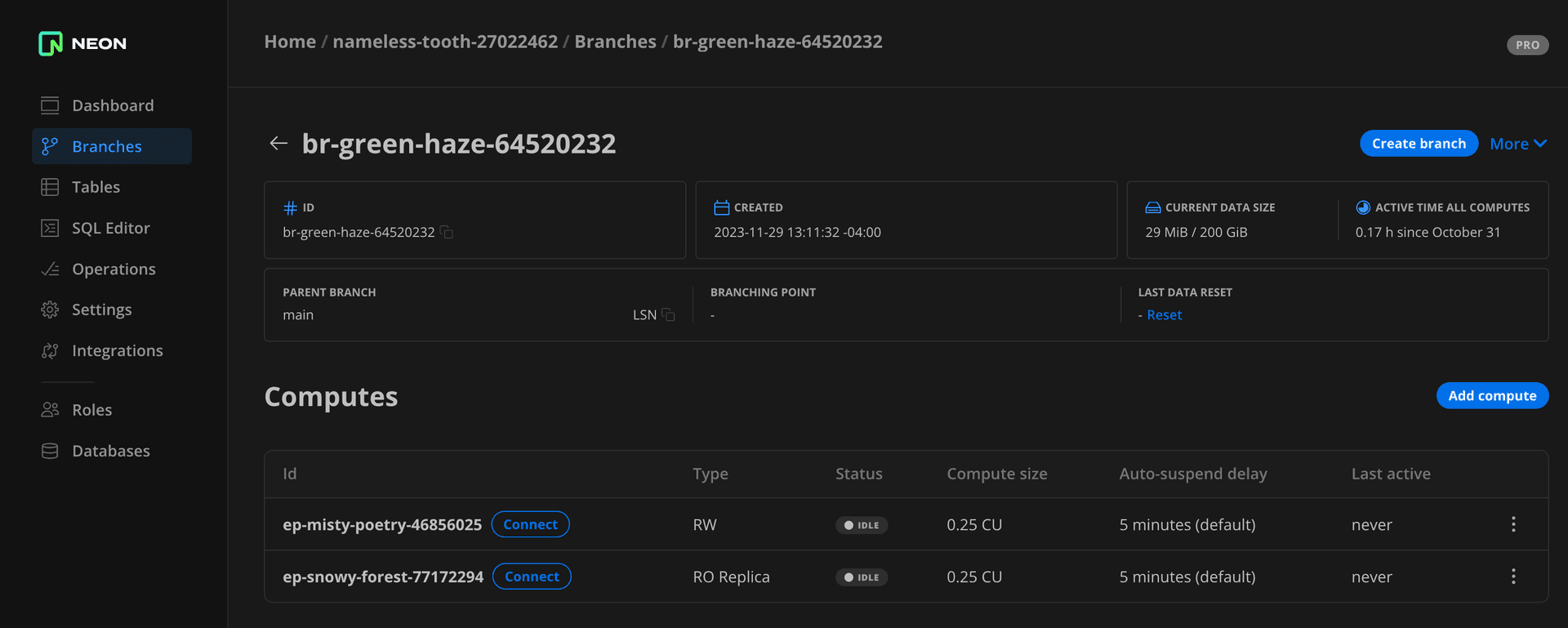
Edit a read replica
You can edit a read replica using the Neon Console or Neon API to change the Compute size or Autosuspend configuration.
To edit a read replica compute using the Neon Console:
- In the Neon Console, select Branches.
- Select a branch.
- Under Computes, identify the read replica compute you want to modify, and click Edit.
- Specify your settings click Save.
Delete a read replica
You can delete a read replica using the Neon Console or Neon API. Deleting a read replica is a permanent action, but you can quickly create a new read replica if you need one.
To delete a read replica using the Neon Console:
- In the Neon Console, select Branches.
- Select a branch.
- On the Computes tab, find the read replica you want to delete.
- Click Edit → Delete.
Default and read replica compute setting synchronization
In a Postgres primary-standby configuration, certain settings should be no smaller on a standby than on the primary in order to ensure that the standby does not run out of shared memory during recovery, as described in the PostgreSQL hot standby documentation. For Neon read replicas, it's no different. The same settings should be no smaller on a read replica compute (the "standby") than on your primary read-write compute (the "primary"). For this reason, the following settings on read replica computes are synchronized with the settings on the primary read-write compute when the read replica compute is started:
max_connectionsmax_prepared_transactionsmax_locks_per_transactionmax_wal_sendersmax_worker_processes
Need help?
Join our Discord Server to ask questions or see what others are doing with Neon. Users on paid plans can open a support ticket from the console. For more detail, see Getting Support.
Last updated on